Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
![How to Start in Safe Mode in Windows 11 [2023]](https://technukti.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/safe.jpg)
Windows 11, the latest operating system from Microsoft, has brought a range of new features and improvements to the table. However, even with the most advanced systems, there may come a time when you need to troubleshoot and diagnose issues with your computer. One effective way to do this is by starting Windows 11 in Safe Mode. Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode that allows you to run Windows with a minimal set of drivers and services, making it an invaluable tool for identifying and resolving various system issues.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the steps to start Windows 11 in Safe Mode. We will also explore why Safe Mode is useful, what it is, and how it can help you in troubleshooting common problems. Whether you’re facing software conflicts, driver issues, or any other problems, this guide will help you navigate through it all. So, let’s get started!
Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode in Windows 11 designed to help you troubleshoot and fix various issues with your computer. When you start your computer in Safe Mode, it loads a minimal set of drivers and services, excluding unnecessary startup programs and features. This stripped-down version of Windows ensures that only essential elements are running, making it easier to diagnose problems that might be caused by third-party software or drivers.
Safe Mode is important for several reasons:
If your computer is experiencing problems, such as crashes, freezes, or software conflicts, Safe Mode can help you determine if these issues are caused by third-party software or drivers. By booting into Safe Mode, you can isolate the problem and take necessary action.
Safe Mode is a valuable tool for removing malware and viruses from your system. Since Safe Mode only loads essential components, it can help you eliminate malicious software that may be affecting your computer’s normal operation.
In Safe Mode, you can easily update or uninstall drivers that are causing issues. It provides a stable environment for making these critical changes to your system.
Safe Mode can help restore your computer to a functional state, allowing you to troubleshoot and resolve problems without the interference of non-essential software and services.
Starting Windows 11 in Safe Mode is a straightforward process. Here are the steps you need to follow:
Windows key on your keyboard to open the Start menu.Enter. This will open the System Configuration tool.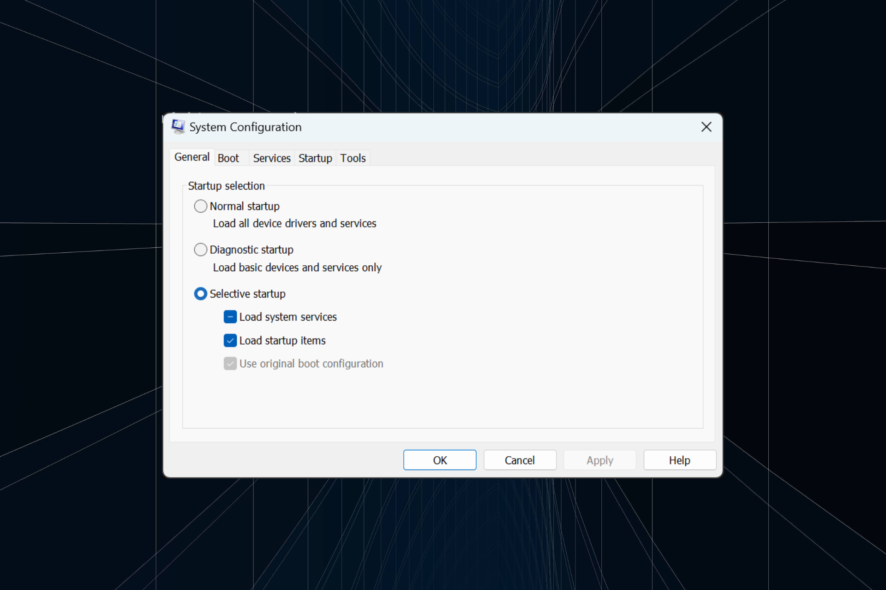



Windows icon in the taskbar or press the Windows key on your keyboard.Shift key on your keyboard.Shift key, click “Restart.”Ctrl + Alt + Delete on your keyboard.Shift key on your keyboard, click “Shut down.”Windows 11 offers different Safe Mode options to suit your specific needs:
This is the most basic Safe Mode option. It loads Windows with a minimal set of drivers and services. Use this mode when you suspect that a recently installed third-party application is causing issues with your system. Safe Mode (Minimal) allows you to isolate and fix problems related to software conflicts.
Safe Mode with Networking is similar to Safe Mode (Minimal), but with one crucial difference: it includes network support. This means you can access the internet and network resources while in this mode. It’s useful for troubleshooting issues related to internet connectivity, downloading drivers, or accessing online resources for problem-solving.
This mode is primarily for advanced users who are comfortable with the Windows command prompt. It loads Windows with the Command Prompt open, allowing you to execute command-line instructions. Safe Mode with Command Prompt is valuable for making advanced repairs or troubleshooting issues that require specific commands.
Now that you know how to start Windows 11 in Safe Mode, let’s explore how you can use it to troubleshoot and resolve various issues.
If you suspect that a recently installed application or update is causing problems, boot your computer into Safe Mode (Minimal) and see if the issues persist. If they don’t, you can be reasonably sure that a third-party program is the culprit. Uninstall or update the problematic software to resolve the issue.
Safe Mode is a powerful tool for eliminating malware and viruses. Use a reputable antivirus or antimalware program to scan and remove malicious software from your system. The minimal set of drivers and services in Safe Mode makes it harder for malware to hide and operate.
If you’re experiencing driver-related problems, boot your computer into Safe Mode (Minimal) and update or uninstall the problematic drivers. This can resolve issues like graphics card glitches, sound problems, or network adapter malfunctions.
When your computer is
experiencing frequent crashes, freezes, or unexplained issues, Safe Mode can help restore functionality. By eliminating third-party software and unnecessary startup items, you can pinpoint and address the root cause of the problem.
Yes, you can access the internet in Safe Mode with Networking. This mode allows network support, enabling you to troubleshoot internet-related issues and download drivers or updates.
While the concept of Safe Mode remains similar, Windows 11 has introduced some changes to the boot process and interface. Methods to access Safe Mode are different from older versions, as outlined in this guide.
To exit Safe Mode, simply restart your computer. It will boot into the normal Windows mode. Alternatively, if you used the System Configuration tool to enable Safe Mode, go back and uncheck the “Safe boot” option.
It’s generally not recommended to install or uninstall software in Safe Mode. Safe Mode is intended for troubleshooting and repairing issues, not for regular software management. It’s best to make these changes in the normal Windows mode.
If you forget your password while in Safe Mode, you will need to reset it through the normal Windows login process. Safe Mode does not provide any special password reset options.
Starting Windows 11 in Safe Mode is a valuable skill for any Windows user. It provides a secure environment to diagnose and resolve various computer issues, ranging from software conflicts to malware removal and driver troubleshooting. Whether you’re an everyday computer user or an advanced technician, understanding how to access and use Safe Mode can save you time and frustration in resolving problems with your system.
By following the methods outlined in this guide and selecting the appropriate Safe Mode option for your issue, you can take control of your Windows 11 system and ensure it runs smoothly, even when faced with challenges. So, the next time you encounter a stubborn problem on your Windows 11 computer, don’t panic—just reboot into Safe Mode and let the troubleshooting begin.
Remember, Safe Mode is your ally in the quest to maintain a healthy and functional Windows 11 system, and this guide is your roadmap to harnessing its power effectively.
Anchor Back Link: If you want to learn more about Windows 11 and its features, visit the official Windows 11 website.
FAQs: If you have any more questions or need further assistance with Windows 11 or Safe Mode, feel free to explore our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) section for more insights and guidance.